As you may know, I decided to develop a mobile soccer game using my game engine. The reason is quite simple. I want to test the features of the game engine and hopefully find as many bugs as possible.
Developing a mobile soccer game has introduced me to the world of Artificial Intelligence. Although I am not an expert in A.I., I have learned a valuable lesson; An A.I. system uses a state machine, and this state machine should be implemented as modular as possible.
State machines are taught using if-then or switch statements. Although such implementation is OK for small projects, it also leads to spaghetti code in complex projects.
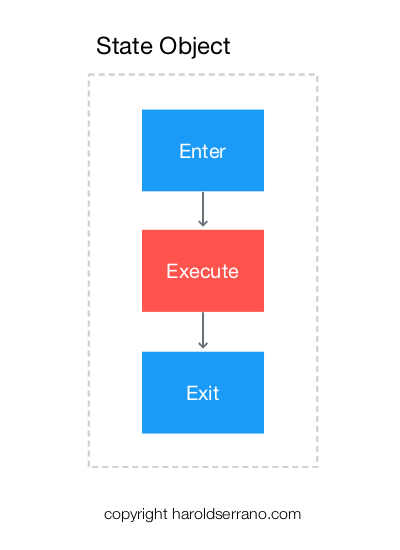
A better way to implement a State Machine is with a Design Pattern known as State Pattern. The pros of using such pattern are that your State machine becomes modular and flexible. That is, you can remove or add as many States into your code without making it a chaotic mess.
Let me show you how to implement a State Pattern.
Note: You can download the project on my Github page so you can follow along.
Create an Abstract State Class
First, implement an abstract State class as shown below:
Abstract State Class
class StateInterface {
public:
virtual ~StateInterface(){};
virtual void enter(Player *uPlayer)=0;
virtual void execute(Player *uPlayer, double dt)=0;
virtual void exit(Player *uPlayer)=0;
};
The "execute" method will perform your "State" operations. The "enter" and "exit" methods are useful methods in an A.I. system. For example, you may have a 3D model that as it enters the "state", it waves his hand. Or it performs a goodbye gestures as it exits the "state."
Implement the concrete State Classes
Then, implement the concrete state classes. In this instance, let's implement a "Walking" and "Running" state class.
Walking State class
void WalkingState::enter(Player *uPlayer){
std::cout<<"Player entering Walking State"<<std::endl;
}
void WalkingState::execute(Player *uPlayer, double dt){
std::cout<<"Executing Walking State"<<std::endl;
}
void WalkingState::exit(Player *uPlayer){
std::cout<<"Player exiting Walking State"<<std::endl;
}
Running State class
void RunningState::enter(Player *uPlayer){
std::cout<<"Player entering Running State"<<std::endl;
}
void RunningState::execute(Player *uPlayer, double dt){
std::cout<<"Executing Running State"<<std::endl;
}
void RunningState::exit(Player *uPlayer){
std::cout<<"Player exiting Running State"<<std::endl;
}
As explained earlier, the "execute" method is the heart of your State operation. It is in this function where most of your logic resides. Moreover, this method will be called continuously until a change of state occurs.
You may notice that the States are implemented as Singletons. You don't have to implement the State classes as singletons, but I usually do.
Implement a State Manager
The State Manager class is responsible for changing the states and keeping track of previous states. This is shown in the snippet below:
State Manager Class
void StateManager::update(double dt){
currentState->execute(player, dt);
}
void StateManager::changeState(StateInterface *uState){
//keep a record of previous state
previousState=currentState;
//call the exit method of the existing state
if (currentState!=NULL) {
currentState->exit(player);
}
//change state to new state
currentState=uState;
//call the entry method of the new state
currentState->enter(player);
}
Before changing to a new state, the manager keeps a copy of the current state. It then calls the "exit" method of the current state. Changes to the new state and calls the "enter" method of the new state.
After the "changeState" method has completed, the manager enters the "update" method, where it continuously calls the "execute" method of the current state.
Putting it all together
Let's implement a simple class called "Player." This object will hold a pointer to the State Manager object. It will also contain a "changeState" and "update" method. Note that these methods delegate its operations to the State Manager member. See snippet below:
Player class
Player::Player(StateManager *uStateManager){
stateManager=uStateManager;
}
Player::~Player(){
}
void Player::update(double dt){
stateManager->update(dt);
}
void Player::changeState(StateInterface *uState){
stateManager->changeState(uState);
}
Finally, let's put the State Pattern in action.
In the "main" function, let's create a state manager object, a player object and let's change the player object state as shown below:
main() Method
//Create a State manager object
StateManager *stateManager=new StateManager();
//Create a player object
Player *player=new Player(stateManager);
//Change the state of the object to a RUNNING state
player->changeState(RunningState::sharedInstance());
//call the update method
player->update(1.0);
//Change the state of the object to a WALKING state
player->changeState(WalkingState::sharedInstance());
//call the update method
player->update(1.0);
When you run the project, the output window will show the player entering, executing and exiting the state as shown below:
- Player entering Running State
- Executing Running State
- Player exiting Running State
- Player entering Walking State
- Executing Walking State
If you want to add a new state, you simply create a new state class, without having the need to modify the if-then/switch statements commonly used in state machines.
State Patterns make the implementation of a state machine very flexible, modular and clean. If 100 years from now, you need to add more states to your project, you won't have to modify the inner workings of your application. Instead, you just create new state classes.
Hope this helps